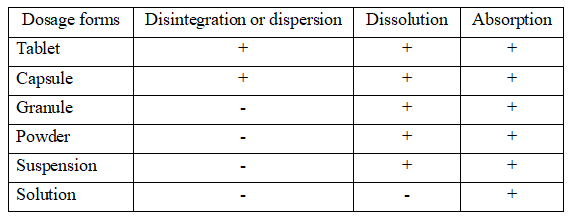
Common solid dosage forms include powder, granules, tablets, capsules, guttate pills, membrane and the like.
Solid dosage forms common feature
(1) Its physical and chemical stability are better than that of liquid preparations and it has low production cost. It is convenient to take and carry the solid preparations.
(2) After dissolving in the body, the medicine can go through the biological membrane and be absorbed into the blood.
Solid dosage forms internal absorption pathway
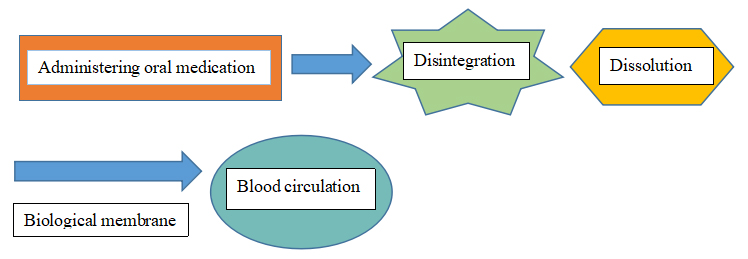
Internal absorption pathway of different dosage forms
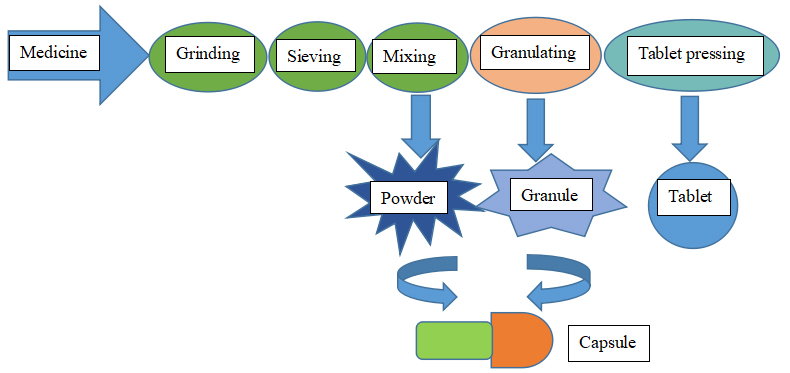
Solid dosage forms preparation technology flow chart
The method of improving medicine dissolution rate
(1) Increase medicine dissolution area by grinding and disintegrating the medicine.
(2) Increase dissolution rate constant by strengthening the stirring of the medicine.
(3) Increase medicine solubility by improving the temperature, change the crystal type and making it into the solid dispersion.
Note: The grinding technology, medicine solid dispersion technology, medicine inclusion technology and the like can effectively increase medicine dissolution rate or dissolution surface area.
Oral preparations absorption speed order
Solution > Suspension > Powder > Granule > Capsule > Tablet > Pill
Powder
Overview
The powder is a powdery preparation which is made of a or several medicine(s) by uniformly mixing, and it can be used externally and internally.
Its classification has three ways as following:
①It can be classified as the medicine quantity into the single powder and the compound powder.
②It can be classified as the dosage situation into the dosage-divided powder and the dosage-no-divided powder.
③It can be classified as the purpose into the solution powder, the boiled powder, the blowing powder, the oral powder, the powder for external use and the like.

The powder has the following features:
①It has a high degree of grinding, large specific surface area, easy dispersion and quick effect.
②It has large coverage area for external use, which can play a role in protection and astringency at the same time.
③It is easy to store,convey and carry.
④It has simple preparation technology and easily controllable dosage which is easy to take the medicine for infants and young children.
⑤It has the features of dispersity, adhesion, agglomeration and hygroscopicity.
The powder preparation
The powder preparation technological process
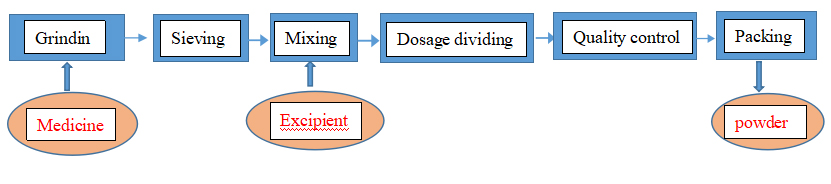
Grinding and sieving
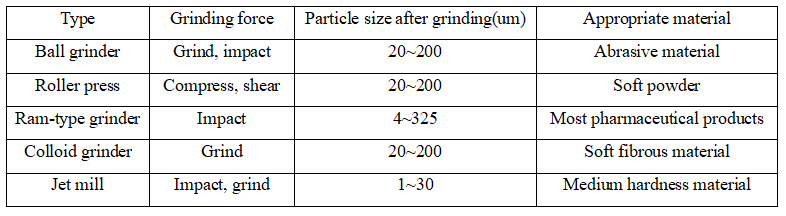
The grinding of solid medicine is to crush large lump material into granule or powder with appropriate size through mechanical force.
Grinding
The significance of grinding:
① It helps to increase the dissolution rate and the biological availability of the poorly soluble medicine.
② It helps to uniform mixing of all ingredients.
③ It helps to improve the dispersity of solid medicine in the liquid, semisolid and gas.
④ It helps to extract effective constituents from natural medicine.
Grinder
Sieving
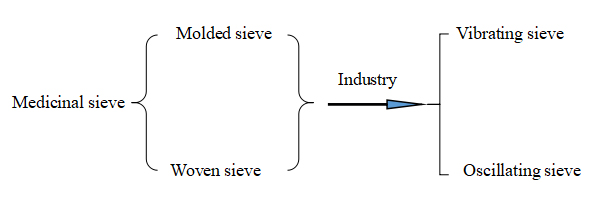
The sieving is to separate the material with screen mesh.
The aim of the sieving is to get uniform particle swarm.
Mixing
The mixing is to uniformly mix the material with more than two ingredients. Its aim is to ensure uniform content, which is one important measure of guaranteeing preparation product quality.
Mixing method
Mixing method in the laboratory: Stirring, grinding, sieving.
Mixing method in the mass production: Stirring and rotation of the container.
Dosage dividing
The dosage dividing is to pack the uniformly mixing material as per the dosage requirement.
Common method: The ocular estimate method, the gravimetric method, and the volumetric method.
Packing and storage
The key point of powder packing and storage is moisture-proof. The moisture absorption property of powder and the measure of preventing moisture absorption are important content of controlling powder quality.
Packing material: Paper, plastic bag and glass bottle.
Storage: Sealing for storage.
Powder quality inspection
(1) Uniformity: Take out of samples with appropriate amount, tile them on the smooth paper with the area of about 5 cm², flatten the surface and observe them in the light. It should be observed that the sample has uniform color without pattern and colour spot.
(2) Moisture: The sample is measured as per the aquametry. Its moisture can not exceed 9.0% except for other special regulation.
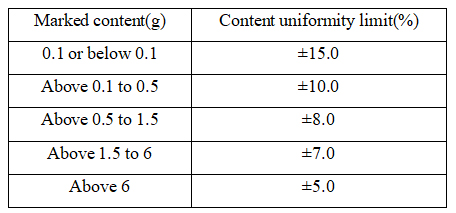
(3) Content uniformity: For the powder with single-dose and one-day-dose, its content uniformity limit should meet the regulation. In addition, the powder should be examined in accordance with “ Microbial Limit Test ” in the appendix of Chinese Pharmacopoeia, and the result should meet the relevant regulations.
Powder content uniformity limit requirement
(4) Hygroscopicity: The powder has large specific surface area, strong hygroscopicity and strong weathering. This has a strong effect on powder quality and medication safety. As a result, the moisture absorption property of the powder and the measure of preventing moisture absorption are important content of controlling powder quality.
The critical relative humidity (CRH) is the characteristic parameter of water-soluble medicine. When the relative humidity of air is higher than the critical relative humidity of the material, the material is easy to absorb moisture. After mixing several kinds of water-soluble medicines, the CRH of the mixture is approximately equal to the product of each ingredient’s CRH. Therefore, the mixing and storage of the class of medicine must be performed to effectively prevent moisture absorption under the circumstance that the relative humidity of air is lower than the CRH of the mixture.
Preparation of various kinds of powder
(1) Ordinary solid medicine powder
(2) Powder containing small doses of medicine
(3) Powder containing the extract
(4) Powder containing eutectic components
(5) Chinese medicine powder
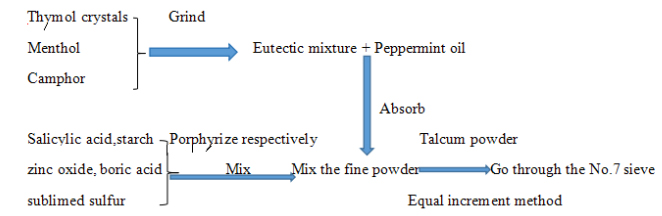
Preparation of the prickly-heat powder
The prickly-heat powder prescription: 0.6 g thymol crystals, 0.6 g menthol, 0.6 ml peppermint oil, 0.6 g camphor, 1.4 g salicylic acid, 4 g sublimed sulfur, 8.5 g boric acid, 6 g zinc oxide, 10 g starch and 100 g talcum powder.
Granule
The granule is a granular preparation which is made of the medicine and appropriate excipients. It is classified as the solubility in water into the soluble granule, the suspension granule and the effervescent granule.The granule can be swallowed directly, and it also can dissolve into the water for drinking. It is convenient to take and carry the medicine. The granule has high dissolution rate and absorption rate.

The feature of the granule
(1) It has poor dispersity, adhesion, agglomeration and hygroscopicity.
(2) The granule is convenient to take, and the colorful, delicious and flavor granule can be made according to the need.
(3) The granule can be coated for moisture resistance, slow release and enteric solubility, and the uniformity of coating must be ensured.
(4) The segregation phenomenon is easy to occur when mixing several kinds of granules, causing inaccurate dosage.
The granule preparation
The preparation technology of the granule is similar to that of the tablet, and the granule is placed into the sachet directly instead of compressing into the tablet.
① Make soft material
② Make wet granule(fluidized-bed granulation)
③ The drying of the wet granule
④ Sieving and grading
⑤ Coating and quality testing
The granule preparation technology―technological process
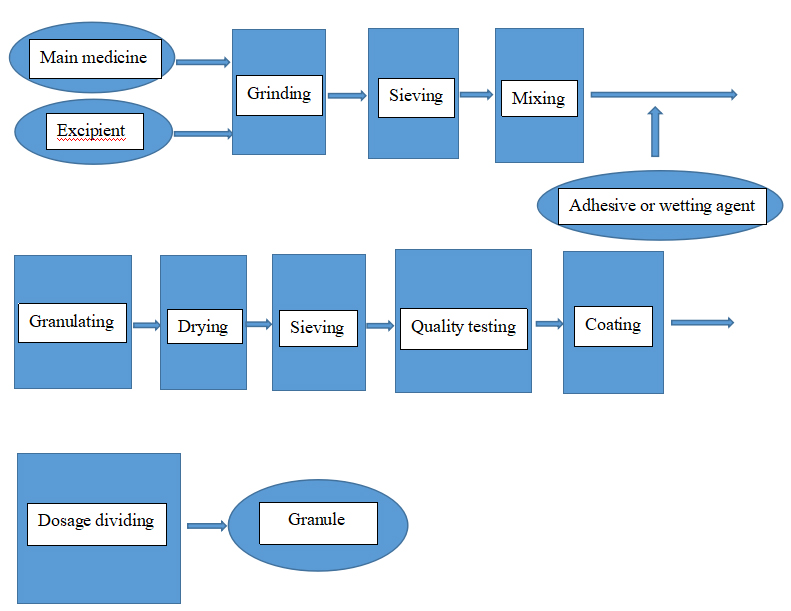
Common excipients for granulation
① Filling agent
② Wetting agent
③ Adhesive
The filling agent includes the diluent (for increasing the weight and volume of the tablet) and the absorbent (for absorbing the liquid in the prescription).
Common filling agent:
Starch
Dextrin
Powdered sugar
Milk sugar
Mannitol and sorbitol (chewable tablet)
Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC)
Pregelatinized starch (compressible starch)
Inorganic salt: Calcium sulfate, pharmaceutical calcium carbonate and so on(absorbent)
Common excipient for granulation―Wetting agent
The wetting agent is a type of liquid which is not sticky in itself. Its role is to wet the tablet material and induce the viscosity of the material.
The type of the wetting agent: Distilled water and ethyl alcohol.
Common excipient for granulation―Adhesive
The adhesive is a type of solid or liquid material which is sticky in itself. Its role is to increase the viscosity of the material.
The type of the adhesive: Starch paste, powdered sugar and syrup, dextrin, cellulose derivative, high-molecular polymer, adhesive cement, microcrystalline cellulose.
Granulating method: Wet granulation and dry granulation
Wet granulation
1. Extruding and sieving for granulation
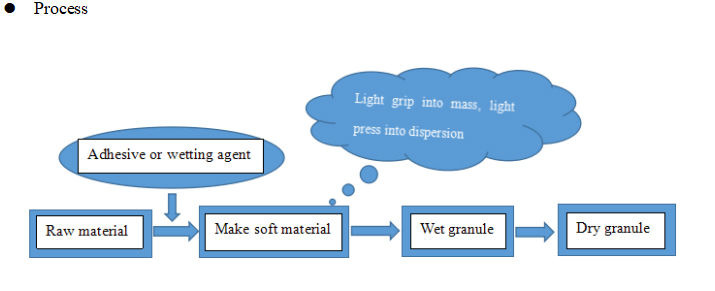
Granulating equipment: Trough type mixer, oscillating granulator, rotary extrusion granulator, and screw extrusion granulator.
2. Rotating granulation
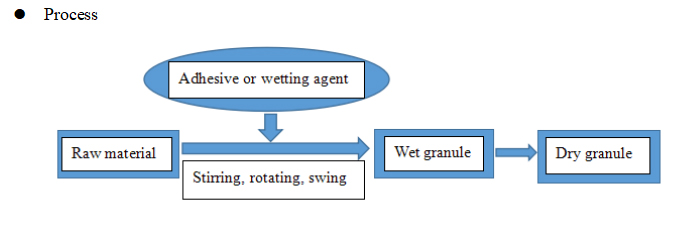
Granulating equipment: Round rotating granulator, tilting rotating granulator, sugarcoating pot, and centrifugal granulator.
3. High speed granulation
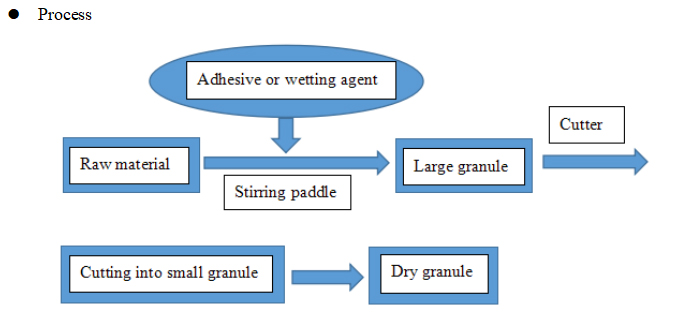
Granulating equipment: High speed stirring granulator.
One step granulation is that the mixing, granulating and drying are performed in the same machine.
(1) Fluidized boiling granulation
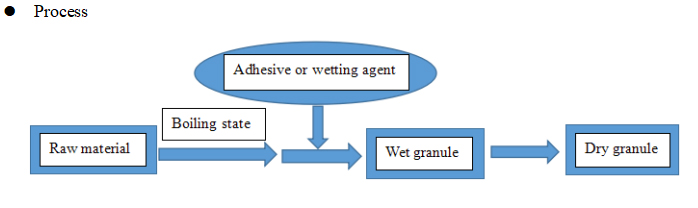
Equipment: Fluidized boiling granulator.
(2) Spray drying granulation
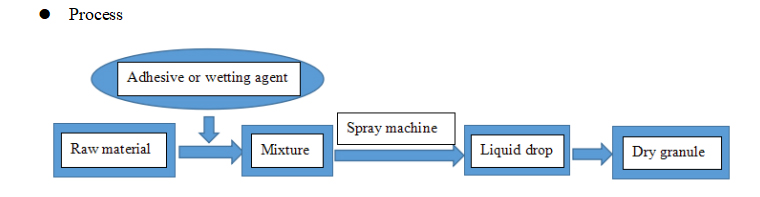
Equipment: Spray dryer.
The method of wet granulation
① Purpose: Multiple unit operations such as mixing, kneading, granulating and drying are completed in the same machine.
② Equipment: Stirring fluidized granulator, rotating fluidized granulator, stirring rotating fluidized granulator.
Dry granulation
Technological process
Material→Pressing into thin pieces or large pieces→grinding into small granule
Preparation method
(1) Rolling method
(2) Double compression method

 English
English

















